Rosenberg J, ole-MoiYoi K, Morse M.
Concept Note: Clinical Background on HIV/AIDS, Malaria, and Tuberculosis.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2016.
AbstractThis concept note provides a clinical overview of three diseases that feature predominantly in our case study collection: HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria. The concept note describes the pathology, causes, and management related to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of each of the diseases.
Learning Objectives: To further students’ and instructors’ understanding of clinical concepts presented in the Global Health Delivery (GHD) Case Collection.
Keyword: Epidemiology, pathology, disease management, monitoring and evaluation, resource allocation, global health policy, partnerships, reatment and prevention.
 Download GHD-C10 Clinical Disease Concept Note
Download GHD-C10 Clinical Disease Concept Note Sue K, Rosenberg J, Weintraub R.
Addressing Tanzania’s Health Workforce Crisis Through a Public-Private Partnership: The Case of TTCIH.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2016.
AbstractSet in rural Tanzania, this case traces the founding and development of the Tanzanian Training Centre for International Health (TTCIH) from the early 2000s through 2015. It begins with an overview of the political, socioeconomic, and epidemiological context of Tanzania, followed by a detailed description of the human resource for health crisis in Tanzania and the landscape of available health care training programs. The case then explores the origins and evolution of TTCIH, launched through a unique collaboration between private industry, a public health institute, local stakeholders and educators, and the Tanzanian Ministry of Health and Social Welfare. It describes the evolution of TTCIH as leaders strive to make it self-sustaining and responsive to Tanzania’s health workforce crisis. The case highlights the challenges of successfully integrating corporate management practices and values into a global health program and the role of strategic leadership to sustain TTCIH.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.
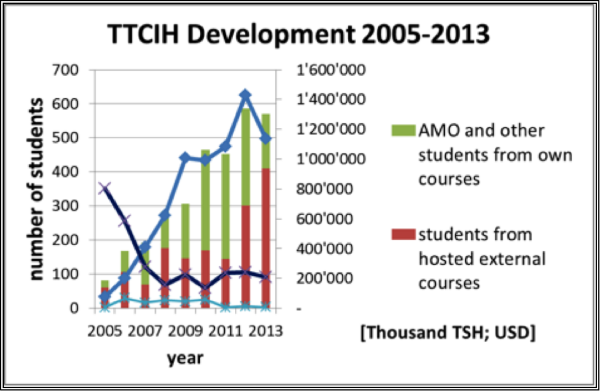
TTCIH Income and Number of Students, 2005–2013
Learning Objectives: A productive class discussion will allow students to appreciate the challenges of designing sustainable, high-quality health training institutions in low-resource settings; the training and resources needed to support task shifting and to address health workforce shortages in health care delivery; and, the importance of maintaining a sound strategy for medical education programs in the midst of changing national health needs and the evolving medical education landscape.
Keywords: Global health, public health, health care delivery, education, government, value creation, Human Resources for Health, health care, nongovernmental organizations, Public-Private partnerships, learning, revenue growth, organizational effectiveness
 Download GHD-034 The Case of TTCIH
Download GHD-034 The Case of TTCIH Brooks P, Rosenberg J, Weintraub R.
The Global Trachoma Mapping Project.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2016.
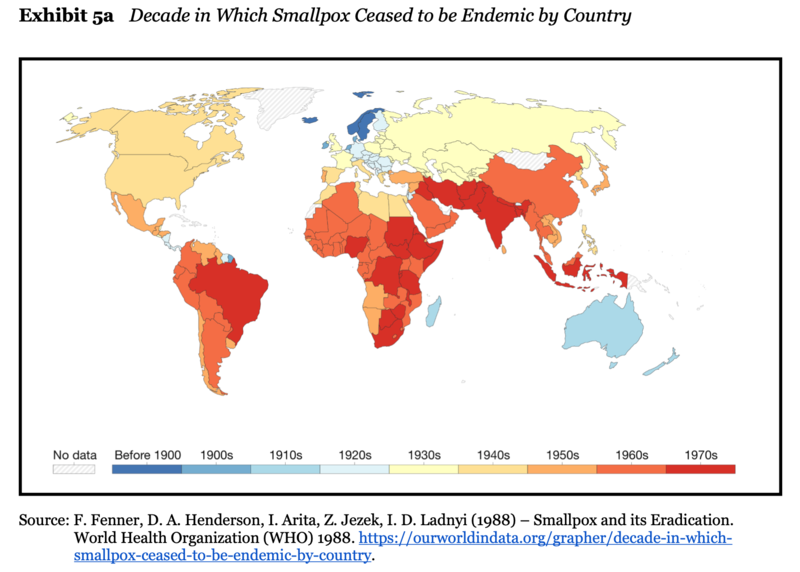
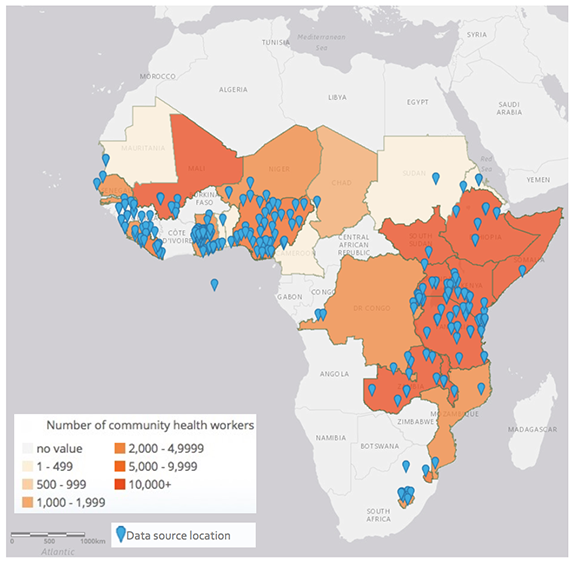
AbstractThis case explores what it took to map the prevalence of trachoma infection in 1,531 districts across 26 countries by directly examining 2.39 million individuals in just three years. Dozens of organizations worked together on the largest standardized mapping project in the world as part of an effort to eliminate blinding trachoma globally by the year 2020. After providing some background on trachoma, early control efforts, and the formation of a global coalition, the case explores the events, strategies, technology, and stakeholders that enabled the mapping project. It describes how the stakeholders worked together, the coordination and management mechanisms used, and the investments required. Given that disease elimination had been achieved only once before, in the case of smallpox, the case asks students to consider how the project’s leaders, Tom Millar and Anthony Solomon, could help maximize returns from trachoma mapping so that the campaign could achieve its ultimate goal of global trachoma elimination within the next five years. Were there ways in which they could leverage efforts to map this neglected tropical disease to inform other disease control programs?
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.
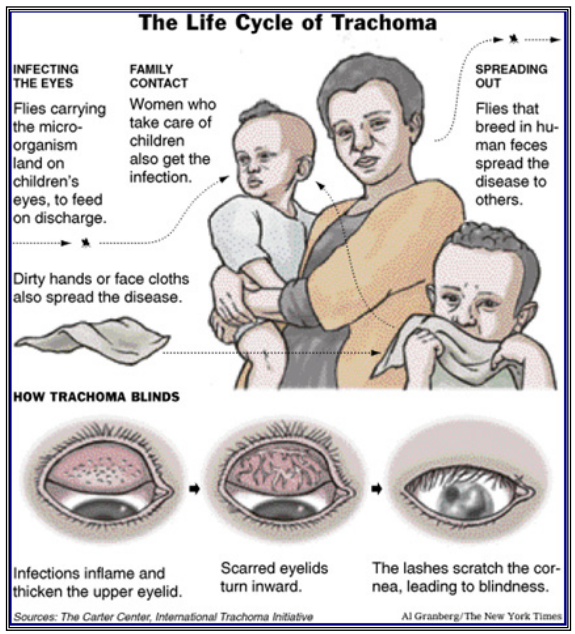
Life Cycle of Trachoma. Source: The Carter Center/Al Granberg, International Trachoma Initiative. Available at http://www.neglecteddiseases.gov/target_diseases/trachoma/.
Learning Objectives: A productive class discussion will allow students to appreciate what contributes to the development of a productive coalition; what it takes to collect quality data at scale; the challenges and benefits of identifying your target population for public health programming; and the tradeoffs between a targeted campaign addressing one disease and bundling efforts for multiple diseases.
Keywords: Disease mapping, disease elimination, multi-sectoral collaboration, electronic data capture
 Download GHD-035 The Global Trachoma Mapping Project
Download GHD-035 The Global Trachoma Mapping Project