Phillips E, Rhatigan J.
Treating Malnutrition in Haiti with Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Foods.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
AbstractThis case describes the introduction of ready-to-use therapeutic foods (RUTFs) to treatment programs for severe acute malnutrition in children six months to five years old. It describes how RUTFs transformed malnutrition treatment in emergency and non-emergency contexts and how their use has evolved since they were introduced in 1999. The case examines RUTF policy in Haiti including the results of a pivotal pilot program and the introduction of RUTFs. The case explores the decision of the chief of Haiti’s Department of Nutrition to use RUTF for the treatment of moderately acute malnutrition in Haiti and leaves readers grappling with the question of how to implement a this policy.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.

Model Plumpy’nut Sachet. Source: http://www.lle.rcs.k12.tn.us/Teachers/guidance_page/Images/plumpybag.jpg. Accessed June 17, 2009. (Exhibit 7 from "Treating Malnutrition in Haiti with Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Foods" case.)
Learning Objectives: To understand the global public health approaches to malnutrition and its prevention, and to examine the role of ready to use therapeutic foods in malnutrition treatment and prevention programs.
Keywords: Childhood malnutrition, health policy implementation
 Download GHD-014 Treating Malnutrition in Haiti with RUTF
Download GHD-014 Treating Malnutrition in Haiti with RUTF May M, Cash R, Rhatigan J.
Tuberculosis in Dhaka: BRAC’s Urban TB Program.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
AbstractThis case examines BRAC’s experience expanding its rural TB program to the urban environment of Dhaka between 2002 and 2008. The case provides background information about Dhaka and describes what TB services existed at the time. The case then describes the expansion of BRAC’s TB program into Dhaka and details innovations in the Urban program. Students should gain an understanding of how these program modifications were a response to the specific challenges the program faced in the urban setting. The case allows an exploration of how successful health care delivery program adapt to new environments.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.
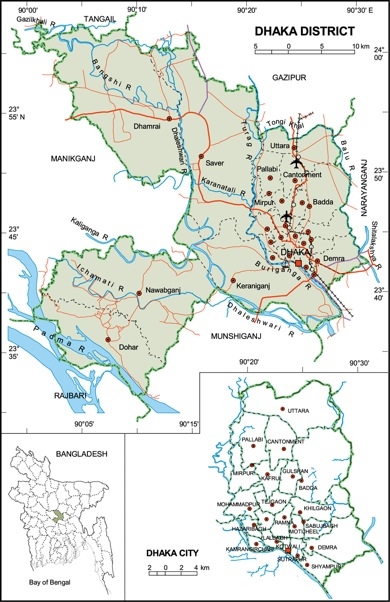
Map of Dhaka. Source: Available at http://www.urpnissues.com/webpage/maps/Districts/13.GIF. (Exhibit 1 in "Tuberculosis in Dhaka: BRAC’s Urban TB Program" case.)
Learning Objectives: To understand how a successful health care delivery program that is uniquely tailored to a particular setting can adapt its operations in a new environment.
Supporting Content: This case is a sequel to BRAC’s Tuberculosis Program: Pioneering DOTS Treatment for TB in Rural Bangladesh.
Keywords: Service delivery innovation, tuberculosis control, urban nongovernmental organizations
 Download GHD-011 BRAC's Urban TB Program
Download GHD-011 BRAC's Urban TB Program Pabo E, Ellner A, Rhatigan J, Lyon E.
Two Years in Hinche.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
AbstractTwo Years in Hinche is a brief supplement to HIV Voluntary Counseling and Testing in Hinche, Haiti. The first case describes an underperforming HIV Voluntary Counseling and Testing Program in government run hospital in Hinche, Haiti, and the decision by a government official to invite, Zanmi Lasante/Partners in Health (ZL/PIH), a non governmental organization, to help revamp the program. After a detailed examination of the program and of the ZL/PIH health care delivery model, the case ends with ZL/PIH agreeing to collaborate with the government to revamp the program. This case describes the subsequent steps ZL/PIH took to increase the amount of patients that received HIV counseling and testing by ten-fold, and to begin an HIV treatment program. It details how they were able to adapt their model for the public sector, improve supply chains, integrate staffs, and build community trust.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.

Learning Objectives: To examine effective strategies for improving uptake of preventive health services in low-resource settings.
Supporting Content: This case is the supplement to HIV Voluntary Counseling and Testing in Hinche, Haiti.
Keywords: Community-based organizations, HIV prevention, government-NGO partnerships
 Download GHD-004B Two Years in Hinche
Download GHD-004B Two Years in Hinche Kleinman S, Rosenberg J, Harris J, Ellner A.
The AIDS Support Organization (TASO) of Uganda.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
Abstract
This case traces the development of The AIDS Support Organization (TASO), a Ugandan non-governmental organization, from 2001 to 2006. One of the first organizations to become involved in HIV/AIDS in the late 1980s, TASO began as a meeting place for people infected and affected by HIV/AIDS, helping people to live positively. The organization provided free counselling, social support, limited medical care, community mobilizing, advocacy and networking. TASO worked alongside government facilities and trained government medical personnel in HIV counselling. After many years, TASO got a new director who brought management skills, a commitment to professionalizing the organization, and a drive to expand services. TASO began incorporating antiretroviral therapy (ART) into its offerings. The ART delivery model combined home and clinic-based care in order to maximize patient adherence. The case follows the development of the organization and scale up of services and raises the question of how to deliver care most cost effectively while maintaining its values and meeting the changing needs of the population and clients.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.

Training health workers to care for HIV/AIDS patients in Uganda. Credit: Sarah Kleinman; TASO
Learning Objectives: Students should learn how a healthcare delivery organization can expand and evolve over time in response to changes in external context and the needs of its clients; how public and private organizations can coordinate to meet the varied needs of a population; and the importance of leadership, management, and strategic vision in creating successful global health programs.
Keywords: Service expansion, Home- and clinic-based care, HIV prevention and treatment.
 Download GHD-008 The AIDS Support Organization (TASO) of Uganda
Download GHD-008 The AIDS Support Organization (TASO) of Uganda Sullivan E, Drobac P, Thompson K, Rodriguez W.
Botswana’s Program in Preventing Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
AbstractThis case traces the development of Botswana’s prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission (PMTCT) program, from its inception as a pilot program in 1999 through its national expansion in 2002 and its struggle to improve outcomes and integrate with broader maternal and child care services through 2008. After providing some background on Botswana, its demographics and health situation, including HIV/AIDS and that national response, the case provides an overview of PMTCT—a critical challenge in global health—and describes the inception of the PMTCT program in Botswana. Readers see the challenges the program faced upon the initial scale-up and explore the key efforts and advances in process and policy that help the country overcome them and become a well known PMTCT success story. The case ends with the program wrestling with a relatively small group of women and their infants who fell through the cracks in the program and several holes in the health system that are preventing the program from eradicating infant HIV completely and tracking its progress.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.

PMTCT Programme vehicle. Credit: Erin Sullivan.
Learning Objectives: To understand the role of a robust strategy, including experimentation, adoption, process improvement, and policy in global health implementation and national scale-up strategies.
Keywords: Health care policy, Horizontal programming, HIV prevention, Translation of research into practice
 Download GHD-007 Botswana's Program for Preventing Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission
Download GHD-007 Botswana's Program for Preventing Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission Dhillon R, Rhatigan J.
The Measles Initiative.
Harvard Business Publishing. 2011.
AbstractThis case examines the work of the Measles Initiative (MI), a consortium of multiple international organizations, in helping catalyze a global effort to reduce worldwide measles-related mortality by expanding delivery of measles vaccinations. After providing background information on the biology of the measles virus and the epidemiology of measles, it recounts the formation of the MI, its partnership structure, its goals, its program design, and its financing. The case focuses on how multilateral global health initiatives coordinate with national governments to improve health care delivery. By 2009, the MI had made significant gains in reducing measles mortality, but was facing decreased funding and was questioning its strategy going forward.
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.
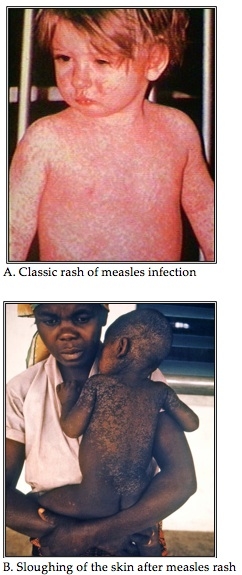
Clinical Presentations of Measles. Image A Source: CDC: Image 132. Public Health Image Library. Available at: http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/details.asp?pid=132. Image B Source: CDC: Image 6887. Public Health Image Library. Available at http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/details.asp?pid=6887. (Exhibit 1 from “The Measles Initiative” case.)
Learning Objectives: To understand how multi-lateral, international disease-control initiatives are designed, coordinated, and financed and to examine how these initiatives interact with national health systems to achieve their objectives.
Keywords: Coordination of multilateral global health initiatives and national governments, international partnerships, measles vaccination campaigns, strategy
 Download GHD-015 The Measles Initiative
Download GHD-015 The Measles Initiative 




