This case explores what it took to map the prevalence of trachoma infection in 1,531 districts across 26 countries by directly examining 2.39 million individuals in just three years. Dozens of organizations worked together on the largest standardized mapping project in the world as part of an effort to eliminate blinding trachoma globally by the year 2020. After providing some background on trachoma, early control efforts, and the formation of a global coalition, the case explores the events, strategies, technology, and stakeholders that enabled the mapping project. It describes how the stakeholders worked together, the coordination and management mechanisms used, and the investments required. Given that disease elimination had been achieved only once before, in the case of smallpox, the case asks students to consider how the project’s leaders, Tom Millar and Anthony Solomon, could help maximize returns from trachoma mapping so that the campaign could achieve its ultimate goal of global trachoma elimination within the next five years. Were there ways in which they could leverage efforts to map this neglected tropical disease to inform other disease control programs?
Teaching Note available through Harvard Business Publishing.
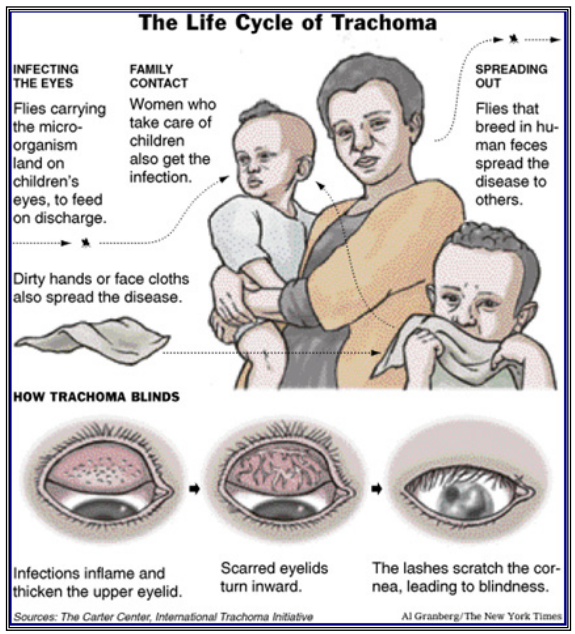
Life Cycle of Trachoma. Source: The Carter Center/Al Granberg, International Trachoma Initiative. Available at http://www.neglecteddiseases.gov/target_diseases/trachoma/.
Learning Objectives: A productive class discussion will allow students to appreciate what contributes to the development of a productive coalition; what it takes to collect quality data at scale; the challenges and benefits of identifying your target population for public health programming; and the tradeoffs between a targeted campaign addressing one disease and bundling efforts for multiple diseases.
Keywords: Disease mapping, disease elimination, multi-sectoral collaboration, electronic data capture